Just back from our field expedition to Bonaire…
Seagrasses are often the “ungly duckling” in marine conservation, and receive disproportionally little attention in the media and in scientific studies when compared to mangroves and coral reefs. However, seagrasses are essential components of coastal zones due to their extremely high productivity and the high biodiversity they support. So time for more research! Inside Lac Bay, Bonaire, seagrasses cover the sea floor and provide a key-habitat to a growing population of endangered green turtles. Additionally, invasive seagrass (originating from the Red Sea) is replacing native seagrasses. Yet the consequences for the seagrass ecosystem services are still unknown. In February, multiple fieldwork projects were conducted on seagrass ecosystem services, and seagrass habitat use of turtles in Lac Bay by a team of local experts (Sabine Engel, STINAPA and team of STCB), together with researchers from Groningen university, NIOZ, NIOO led by Marjolijn Christianen*.

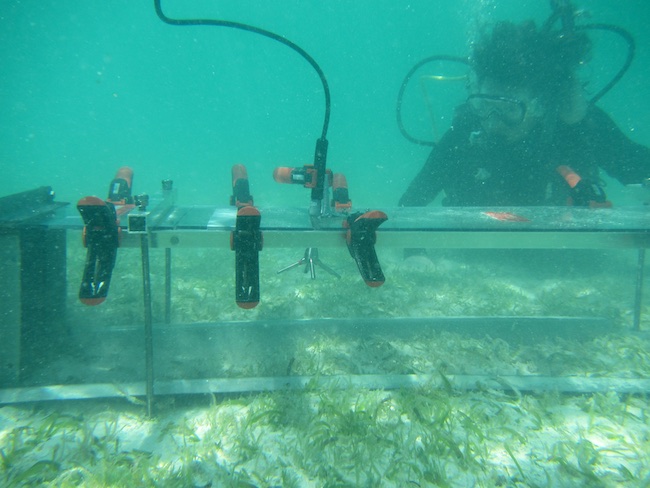
It started with the final measurements of a sea turtle-exclosure study. In the middle of Lac Bay seagrass plots were protected against turtle grazing during the last 1 ½ years to study the impact of grazing on seagrass functioning and the expansion of invasive seagrass. Although results are still to be analysed first results show that grazing may impact the expansion rates of invasive seagrass. It was clear that sea turtles were waiting for the underwater cages to be removed, and the long leaves were directly eaten by the turtles.


In the last 2 years, multiple green turtles were tagged with satellite transmitters to study the movement on foraging habitats in the Dutch Caribbean. In Lac Bay, green turtles spend much of the daytime grazing on seagrass meadows and they often revisit the same site. These turtle hotspots were checked and monitored for species cover, grazing marks and isotope samples were collected. Turtles maintain their own underwater gardens and clip the grass short so that they can eat nitrogen rich fresh leaves. At night, they return to the reef to rest on the coral reef outside of the bay.
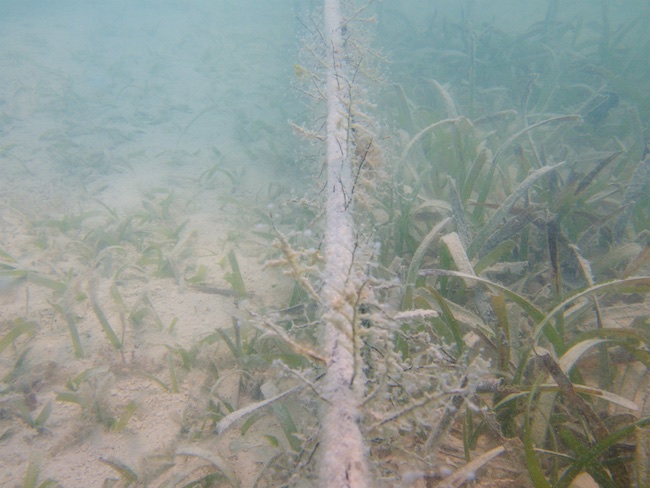

Finally, a pilot experiment was installed to test the use of biodegradable plastic sheets for seagrass restoration as part of a global initiative. This method for ecosystem restoration (“BESE”) is currently being developed by Bureau Waardenburg and Radboud University. A square 1m2 plastic structure is installed either below the sediment or on top of the sediment and seagrass shoots (Thalassia testudinum) are planted in the middle. Instead of transplanting large areas, this method temporarily facilitates seagrasses by simulating positive feedback mechanisms (e.g. reducing hydrodynamics, predation, macroalgae cover) that often naturally occur in seagrass meadows. After bridging the establishment threshold by expanding through the structure, the BESE should break down and seagrass itself can take over. The BESE will be monitored the next year by Sabine Engel (STINAPA).
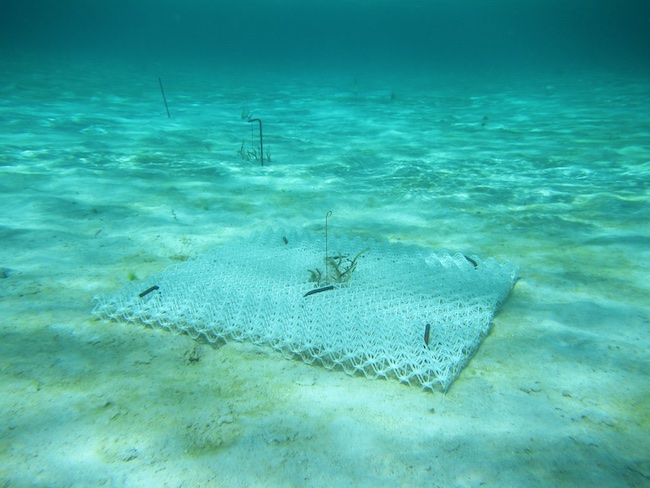


All photos except the first picture: credit Marjolijn
*NWO program Ecology and conservation of green and hawksbill turtles in the Dutch Caribbean.
